
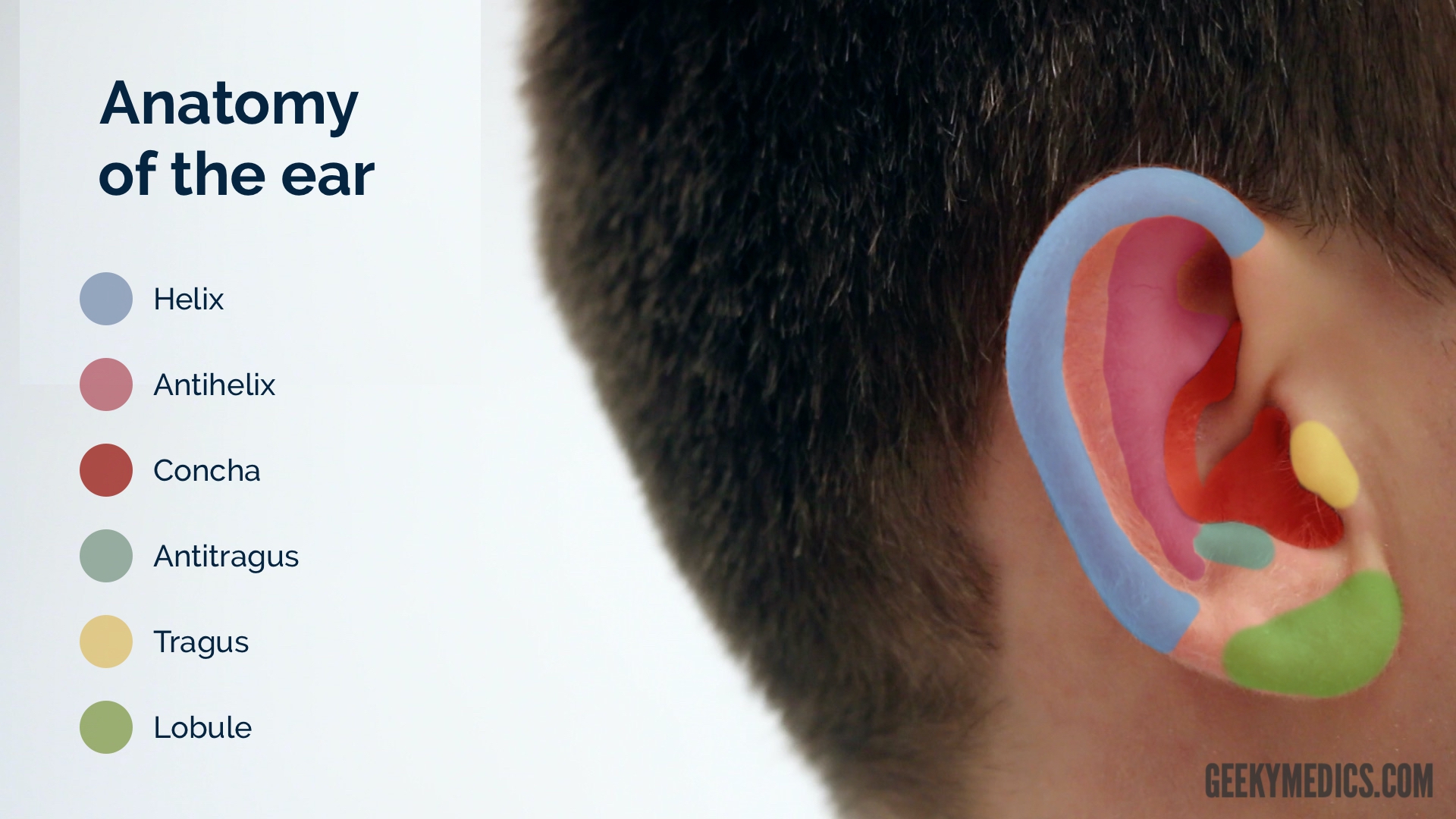
94 dB SPL), the vibratory displacement amplitude of the stapes still measures only 30 nm (in the frequency range 100–1000 Hz) (Hüttenbrink, 1988a, 1995). While at the hearing threshold, vibration amplitudes of the TM are in the pico‐ to nanometer range (smaller than the diameter of a hydrogen molecule), the TM is displaced by up to 1 mm during changes in static pressure (blowing your nose, swallowing, etc.). There, the energy level is so low that a further improvement in sensitivity would be pointless, as then the bouncing of molecules on the TM (by Brownian motion) would be audible. At the hearing threshold, the pressure and amplitude are a millionfold smaller than the loudest tolerable sound. Tympanic membrane (TM), ossicular chain and inner ear represent a highly complex sound pressure wave receiver, whose dynamics are unmatched by any other sense organ. The middle ear is in many circumstances a remarkable organ. The importance of the hearing sense for the social life of man was aptly described by Immanuel Kant: ‘Blindness separates people from things. Next to the sense of sight, the sense of hearing is our most important biological source of information. In addition to the acoustic organ, it also houses the equilibrium organ and thus forms the basis of two human sensory systems. From the evolutionary standpoint, the ear represents the most important warning sensor of the body, a function which it combines with its fundamental role in social communication. The ear is an accurate, powerful and reliable instrument of perception. To minimize risks, a solid knowledge of and respect for neurootologic structures is essential for an otosurgeon who must train him‐ or herself intensively on temporal bones before performing surgery on a patient. Above all, both middle ear diseases and surgery can be associated with a number of complications the most important ones being hearing deterioration or deafness, dizziness, facial palsy and life‐threatening intracranial complications. Surgery is always individualized to the case and there is no one‐fits‐all strategy. Modern techniques for reconstruction of the ossicular chain aim for best possible hearing improvement using delicate alloplastic titanium prostheses, but a number of prosthesis‐unrelated factors work against this intent. Of these, perforations of the tympanic membrane, chronic otitis media, tympanosclerosis and cholesteatoma are encountered most often in clinical practice.

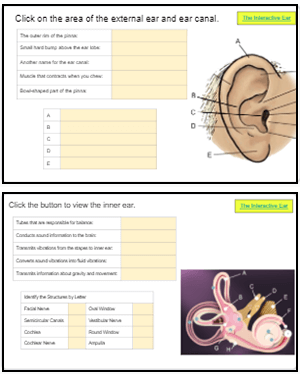
The complex anatomy means a challenge for the otosurgeon who moves between preservation or improvement of highly important functions (hearing, balance, facial motion) and eradication of diseases. Middle ear surgery is strongly influenced by anatomical and functional characteristics of the middle ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
